Judaism and Christianity Venn Diagram: Exploring Similarities and Differences. This analysis delves into the historical roots, beliefs, practices, and relationship between these two influential religions, providing a comprehensive understanding of their shared and distinct characteristics.
Through a comparative lens, this essay examines the core beliefs of monotheism, the nature of God, and the role of Jesus. It explores the similarities and differences in religious practices, such as prayer, rituals, and dietary laws, highlighting how these beliefs and practices shape the daily lives of adherents.
Origins and Historical Development
Judaism and Christianity share a common historical root in the ancient Near East. Judaism emerged as a distinct religion around the 1st millennium BCE, with its origins in the covenant between God and the patriarch Abraham. Christianity, on the other hand, emerged as a sect within Judaism in the 1st century CE, founded by Jesus of Nazareth.
The development of both religions has been influenced by a variety of factors, including the political and cultural context of the time, as well as the influence of other religions and philosophies. Judaism has been shaped by its interaction with ancient Egyptian, Babylonian, and Persian cultures, while Christianity has been influenced by Greek and Roman thought.
Key Events in the Development of Judaism and Christianity
- c. 2000 BCE:Abraham’s covenant with God
- c. 1200 BCE:Exodus from Egypt and the giving of the Torah
- c. 1000 BCE:Establishment of the Israelite kingdom
- 586 BCE:Babylonian conquest of Jerusalem and destruction of the First Temple
- 538 BCE:Return from Babylonian exile and rebuilding of the Second Temple
- c. 1 CE:Birth of Jesus of Nazareth
- c. 30 CE:Crucifixion and resurrection of Jesus
- c. 70 CE:Roman destruction of Jerusalem and the Second Temple
- c. 100 CE:Completion of the Hebrew Bible
- c. 300 CE:Completion of the New Testament
Beliefs and Practices
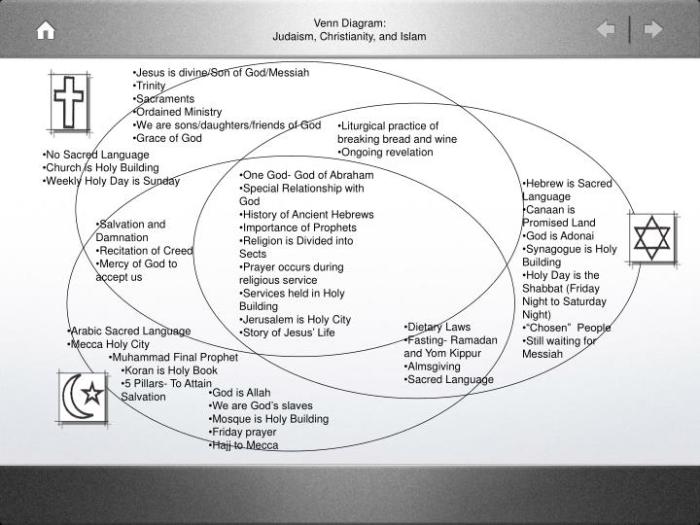
Judaism and Christianity share a common heritage and a belief in one God. However, there are also significant differences between the two religions, particularly in their beliefs about Jesus and the role of the Torah.
Judaism is a monotheistic religion that believes in one God, who is all-powerful, all-knowing, and all-good. Jews believe that God created the world and everything in it, and that He continues to guide and protect His people. The Torah, or the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, is the central religious text of Judaism and contains the laws and commandments that God gave to the Israelites.
Christianity is also a monotheistic religion that believes in one God. However, Christians believe that Jesus is the Son of God and that He came to Earth to save humanity from sin. Christians believe that Jesus died on the cross and was resurrected three days later, and that through His death and resurrection, they can be forgiven of their sins and receive eternal life.
Similarities and Differences in Religious Practices
Judaism and Christianity have many similarities in their religious practices, such as prayer, rituals, and dietary laws. Both religions believe in the importance of prayer, and both have specific prayers that are said at different times of the day. Both religions also have rituals that are performed on special occasions, such as the Sabbath and Passover.
In addition, both religions have dietary laws that restrict what foods can be eaten.
However, there are also some differences in the religious practices of Judaism and Christianity. For example, Jews do not believe in the Trinity, which is the Christian belief that God is three persons in one: the Father, the Son, and the Holy Spirit.
Jews also do not believe that Jesus is the Son of God, and they do not worship him as God.
How Beliefs and Practices Shape the Daily Lives of Adherents, Judaism and christianity venn diagram
The beliefs and practices of Judaism and Christianity have a significant impact on the daily lives of adherents. For example, the Jewish Sabbath is a day of rest and worship, and Jews are not allowed to work or engage in any other activities that would be considered labor.
Christians also have a day of rest, which is Sunday, and they typically attend church services on that day.
The dietary laws of Judaism and Christianity also have a significant impact on the daily lives of adherents. For example, Jews are not allowed to eat pork or shellfish, and they must slaughter animals in a specific way. Christians, on the other hand, are not subject to the same dietary restrictions.
Sacred Texts and Traditions
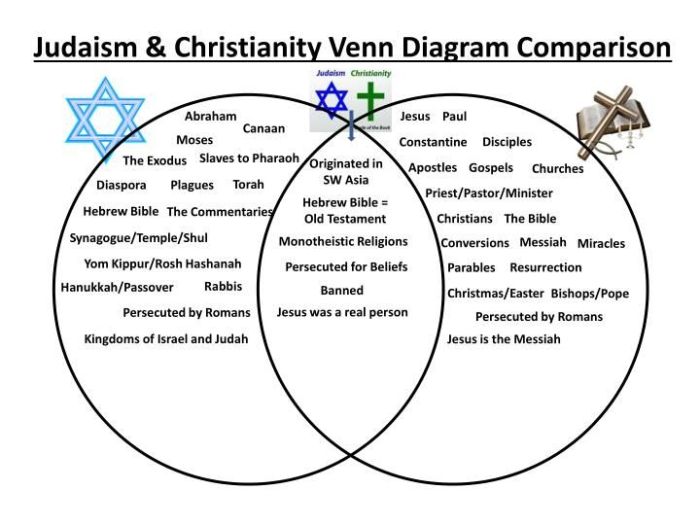
The sacred texts and oral traditions of Judaism and Christianity play a pivotal role in shaping the beliefs, practices, and development of both religions. These texts provide a foundation for religious thought, guide religious practices, and serve as a source of authority and inspiration for followers.
Hebrew Bible and the New Testament
The Hebrew Bible, also known as the Tanakh, is the central sacred text of Judaism. It consists of three main sections: the Torah (Law), the Nevi’im (Prophets), and the Ketuvim (Writings). The Hebrew Bible contains the foundational stories, laws, and teachings of the Jewish faith.
The New Testament, on the other hand, is the primary sacred text of Christianity. It consists of four Gospels, which recount the life and teachings of Jesus Christ, as well as various letters, epistles, and the Book of Revelation. The New Testament provides the basis for Christian beliefs, including the divinity of Jesus, the importance of faith, and the concept of salvation.
Oral Traditions and Interpretations
In addition to written texts, both Judaism and Christianity have rich oral traditions that have influenced religious beliefs and practices. In Judaism, the Oral Torah, also known as the Mishnah and Talmud, contains interpretations and expansions of the written Torah, providing guidance on religious laws and practices.
In Christianity, oral traditions include early creeds, hymns, and liturgical practices that have shaped the development of Christian doctrine and worship. These traditions have been passed down through generations, shaping the understanding and interpretation of the written texts.
Influence on Religious Thought and Practice
The sacred texts and oral traditions of Judaism and Christianity have had a profound influence on the development of religious thought and practice. The Hebrew Bible has provided the foundation for Jewish laws, rituals, and ethical teachings, while the New Testament has shaped Christian beliefs about salvation, grace, and the nature of God.
These texts continue to be studied, interpreted, and debated, providing a source of inspiration, guidance, and authority for followers of both religions.
Relationship between Judaism and Christianity

Judaism and Christianity share a complex and multifaceted relationship that has been shaped by both cooperation and conflict throughout history. The two religions have influenced each other’s beliefs, practices, and traditions, and their interactions have played a significant role in the development of both.
Historical Relationship
Judaism and Christianity emerged from a common historical context, with Christianity originating as a movement within Second Temple Judaism. Initially, there was a period of cooperation and exchange between the two groups, as evidenced by the presence of Jewish Christians in the early Church.
However, tensions gradually arose as Christianity diverged from its Jewish roots and sought to establish its own distinct identity.
Over the centuries, the relationship between Judaism and Christianity has been marked by both periods of persecution and tolerance. In the Roman Empire, Christians faced persecution from both Jewish and Roman authorities. After the conversion of Constantine to Christianity, the Roman Empire became predominantly Christian, and Jews faced increasing discrimination and persecution.
This persecution continued throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era.
Theological Debates and Controversies
Theological debates and controversies have also shaped the relationship between Judaism and Christianity. One of the central issues of contention has been the nature of Jesus Christ. Christians believe that Jesus is the Messiah and the Son of God, while Jews do not accept this claim.
Other theological differences include the role of the Torah, the nature of salvation, and the relationship between God and humanity.
Influences on Development
Despite their differences, Judaism and Christianity have also influenced each other’s development. Christianity borrowed many of its core beliefs and practices from Judaism, including the concept of monotheism, the Ten Commandments, and the importance of social justice. Judaism, in turn, has been influenced by Christian thought and practices, particularly in the areas of liturgy and ethics.
Similarities and Differences
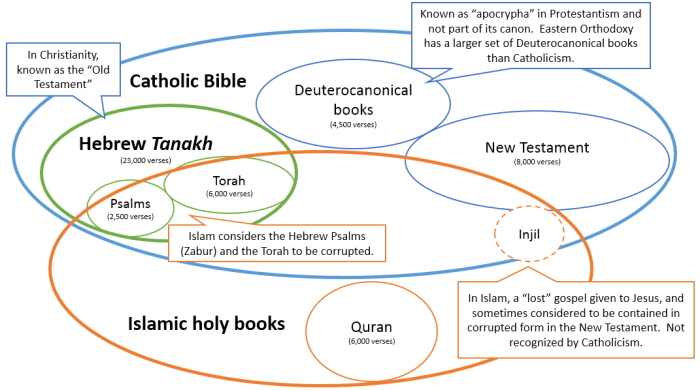
Judaism and Christianity share a rich history and common roots, yet they also have distinct beliefs and practices. This Venn diagram illustrates the key similarities and differences between these two religions.
Shared Beliefs:
- Monotheism: Belief in one God
- Ethical Monotheism: Belief that God is a moral being who demands ethical behavior
- Covenant: A special relationship between God and his people
- Prophecy: Belief that God reveals his will through prophets
Shared Practices:
- Prayer: Communicating with God
- Worship: Expressing devotion to God
- Sacrament: A religious ceremony that symbolizes a sacred event
- Observance of Holy Days: Commemorating important events in religious history
Shared Values:
- Justice
- Compassion
- Peace
- Love
Differences:
- Christology:Christianity believes that Jesus is the Messiah and the Son of God, while Judaism does not.
- Trinity:Christianity believes in the Trinity (God the Father, God the Son, and God the Holy Spirit), while Judaism believes in one God.
- Original Sin:Christianity believes that all humans are born with a sinful nature, while Judaism does not.
- Salvation:Christianity believes that salvation is through faith in Jesus Christ, while Judaism believes that salvation is through obedience to the Law.
These similarities and differences have implications for interfaith dialogue and understanding. By recognizing the shared beliefs, practices, and values between Judaism and Christianity, we can build bridges of respect and cooperation. At the same time, we must also be mindful of the differences between the two religions and approach interfaith dialogue with sensitivity and humility.
Contemporary Issues and Perspectives: Judaism And Christianity Venn Diagram
Contemporary issues and perspectives are significantly shaping Judaism and Christianity, influencing their beliefs, practices, and relationships. These religions are adapting to changing social and cultural contexts, addressing issues such as religious diversity, social justice, and the role of technology.
One key issue is the rise of religious diversity and interfaith dialogue. As societies become increasingly multicultural, Jews and Christians are engaging with people of other faiths, leading to a greater understanding and appreciation of different religious traditions.
Interfaith Cooperation
- Interfaith organizations promote dialogue and cooperation between different religious groups, fostering mutual respect and understanding.
- Joint initiatives, such as community service projects and educational programs, bring people of different faiths together, building bridges and breaking down stereotypes.
Another significant issue is the role of social justice in religious practice. Both Judaism and Christianity emphasize the importance of compassion and helping those in need.
Social Justice Initiatives
- Religious organizations are actively involved in social justice movements, advocating for the poor, marginalized, and oppressed.
- Interfaith coalitions address issues such as poverty, homelessness, and environmental degradation, bringing together people of different faiths to work towards common goals.
Furthermore, technology is playing an increasingly important role in religious life. Social media and online platforms provide new ways for Jews and Christians to connect, share their beliefs, and engage in religious practices.
Technology and Religious Practice
- Virtual religious services and online communities allow people to participate in religious activities from anywhere, making them more accessible and inclusive.
- Digital resources, such as online Torah study and Bible commentary, provide convenient access to religious texts and teachings.
These contemporary issues and perspectives are shaping the future of Judaism and Christianity, fostering greater interfaith cooperation, emphasizing social justice, and embracing technology to enhance religious practice.
Key Questions Answered
What is the significance of the Hebrew Bible and the New Testament in Judaism and Christianity?
The Hebrew Bible (Tanakh) is the foundational sacred text of Judaism, while the New Testament is central to Christianity. These texts provide the basis for religious beliefs, practices, and moral teachings, shaping the spiritual lives of adherents.
How have contemporary issues influenced Judaism and Christianity?
Contemporary issues such as social justice, interfaith dialogue, and the role of women have influenced the beliefs, practices, and relationships between Judaism and Christianity. These issues have sparked discussions on religious pluralism, the need for inclusivity, and the adaptation of religious traditions to changing social contexts.