In the tapestry of colonial America, the experiences of women in New England and the Chesapeake stand out as distinct threads. Compared to women in colonial chesapeake new england women unveils the intricate social, legal, and domestic landscapes that shaped their lives, revealing both striking similarities and profound differences.
From the legal protections afforded to women in New England to the economic opportunities available in the Chesapeake, this exploration delves into the nuances that defined the female experience in these two pivotal regions.
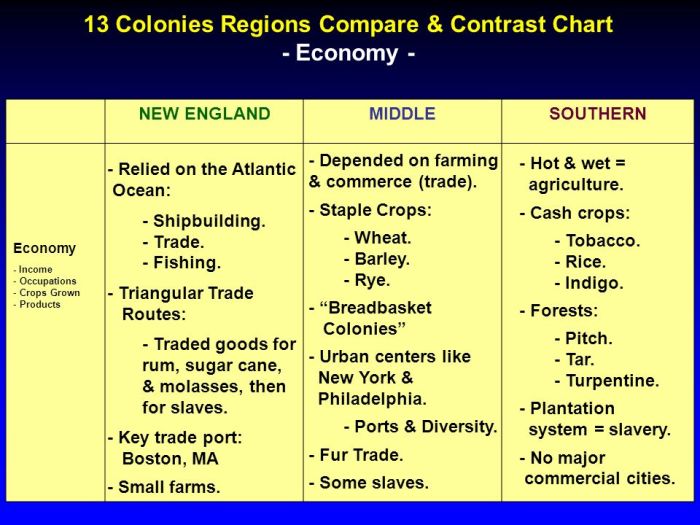
Social Status and Roles
Women in colonial Chesapeake and New England occupied distinct social positions and fulfilled different roles within their respective societies.
Chesapeake, Compared to women in colonial chesapeake new england women
- Lower social status compared to men due to patriarchal society.
- Primarily responsible for domestic duties, such as childrearing, cooking, and cleaning.
- Limited opportunities for education and economic advancement.
New England
- Slightly higher social status than Chesapeake women due to Puritan influence.
- Expected to be literate and contribute to the community through religious activities.
- Some opportunities for economic independence, such as running small businesses or engaging in skilled trades.
Legal Rights and Protections
The legal frameworks and protections afforded to women in colonial Chesapeake and New England varied significantly.
Chesapeake, Compared to women in colonial chesapeake new england women
- Few legal rights or protections.
- Women could not own property or make contracts in their own name.
- Limited recourse in cases of domestic violence or sexual assault.
New England
- Greater legal protections than Chesapeake women.
- Allowed to own property and make contracts under certain conditions.
- Had some recourse in cases of domestic violence or sexual assault.
Economic Opportunities
Women’s economic opportunities in colonial Chesapeake and New England differed based on the region’s economic activities and social norms.
Chesapeake, Compared to women in colonial chesapeake new england women
- Limited economic opportunities outside of domestic labor.
- Some women engaged in small-scale farming or craft production.
- Few opportunities for formal education or skilled trades.
New England
- Greater economic opportunities than Chesapeake women.
- Could engage in a wider range of occupations, including teaching, nursing, and skilled trades.
- Had access to some forms of formal education, such as literacy classes.
Education and Literacy
Access to education and literacy rates for women in colonial Chesapeake and New England differed considerably.
Chesapeake, Compared to women in colonial chesapeake new england women
- Very low literacy rates among women.
- Few opportunities for formal education.
- Women were discouraged from pursuing intellectual pursuits.
New England
- Higher literacy rates than Chesapeake women due to Puritan emphasis on education.
- Access to literacy classes and informal education opportunities.
- Some women pursued higher education and became scholars or writers.
Family Life and Domestic Roles
The roles and responsibilities of women within the family and household varied between colonial Chesapeake and New England.
Chesapeake, Compared to women in colonial chesapeake new england women
- Women had limited authority within the family.
- Primarily responsible for domestic duties and childrearing.
- Had little say in family decisions or property ownership.
New England
- Women had slightly more authority within the family.
- Expected to be active in community and religious life.
- Could sometimes inherit property and make decisions about family finances.
Religious Beliefs and Practices: Compared To Women In Colonial Chesapeake New England Women

The religious affiliations and practices of women in colonial Chesapeake and New England were influenced by the region’s dominant religious beliefs.
Chesapeake, Compared to women in colonial chesapeake new england women
- Anglicanism was the dominant religion, with women playing a limited role in religious life.
- Few opportunities for women to participate in religious activities or leadership.
- Some women practiced folk religion or other non-Anglican faiths.
New England
- Puritanism was the dominant religion, which emphasized women’s literacy and participation in religious life.
- Women could attend church services, participate in prayer groups, and read religious texts.
- Some women became active in religious reform movements, such as the Great Awakening.
Q&A
How did women’s legal rights differ between Chesapeake and New England?
In New England, women had more legal protections, such as the right to own property and the right to sue in court. In Chesapeake, women had fewer legal rights and were subject to the authority of their husbands.
What were the main economic opportunities for women in colonial Chesapeake and New England?
In Chesapeake, women were primarily involved in domestic work and agriculture. In New England, women had more economic opportunities, such as working in trade and manufacturing.
How did women’s roles within the family differ between the two regions?
In Chesapeake, women were primarily responsible for childcare and domestic work. In New England, women had more responsibilities within the family, such as managing the household and educating the children.