Lewis structure for ionic compounds worksheet with answers – Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of Lewis structures for ionic compounds with this comprehensive worksheet and answer key. Immerse yourself in the fundamental concepts of Lewis structures, delve into the intricacies of ionic compound formation, and master the art of drawing accurate Lewis structures for these fascinating chemical entities.
As we unravel the mysteries of ionic bonding, we will explore the limitations of Lewis structures in representing these compounds and uncover the diverse applications of Lewis structures in understanding their behavior. Prepare to expand your knowledge and deepen your comprehension of ionic compounds through this engaging and informative worksheet.
1. Lewis Structure Fundamentals
Lewis structures are a way of representing the bonding and lone pairs of electrons in a molecule or ion. They are named after Gilbert N. Lewis, who developed them in 1916.
The octet rule is a chemical rule of thumb that states that atoms tend to form chemical bonds in such a way that they have eight electrons in their valence shells. This is because eight electrons is a stable configuration, and atoms tend to be most stable when they have a full valence shell.
To draw a Lewis structure, you first need to determine the total number of valence electrons in the molecule or ion. Then, you need to arrange the atoms in a way that satisfies the octet rule. Finally, you need to draw the bonds between the atoms.
2. Ionic Compounds

Ionic compounds are compounds that are formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. The atom that gives up electrons becomes a positive ion, and the atom that receives electrons becomes a negative ion.
Ionic compounds are typically formed between a metal and a non-metal. The metal atom loses electrons to achieve a stable octet configuration, and the non-metal atom gains electrons to achieve a stable octet configuration.
Ionic compounds are typically hard, brittle, and have high melting points. They are also good conductors of electricity.
3. Lewis Structures for Ionic Compounds
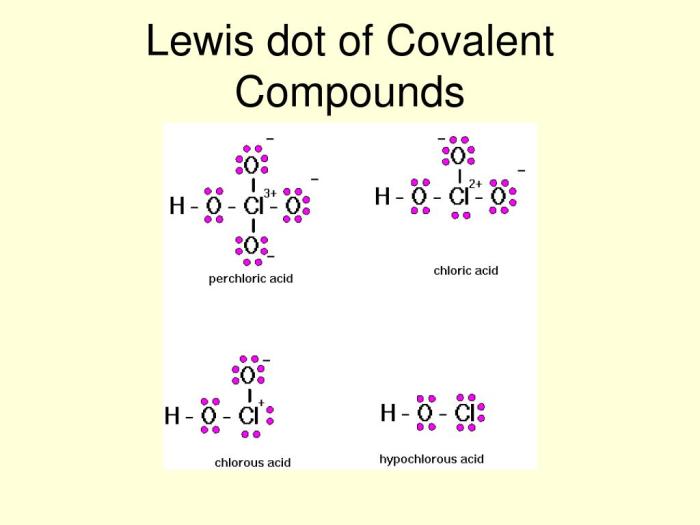
Lewis structures can be drawn for ionic compounds, but they must be modified to account for the transfer of electrons. In a Lewis structure for an ionic compound, the positive ion is represented by its symbol, and the negative ion is represented by its symbol in square brackets.
For example, the Lewis structure for sodium chloride (NaCl) is:
“`Na +[Cl] –“`
In this Lewis structure, the sodium ion has lost one electron, and the chloride ion has gained one electron.
Lewis structures for ionic compounds can be used to predict the properties of the compounds. For example, the Lewis structure for NaCl shows that the compound is composed of a positive ion and a negative ion. This indicates that NaCl is a polar compound, meaning that it has a separation of charge.
4. Practice Worksheet: Lewis Structure For Ionic Compounds Worksheet With Answers
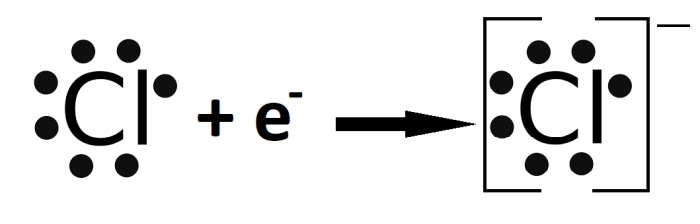
Create a Lewis structure worksheet for ionic compounds. Include a variety of ionic compounds, such as NaCl, KCl, CaO, and MgO.
Provide an answer key for the worksheet.
5. Extensions
Discuss the applications of Lewis structures for ionic compounds.
Explore advanced concepts related to Lewis structures for ionic compounds, such as resonance and molecular orbitals.
Provide additional resources for further learning.
FAQ Insights
What is the octet rule?
The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain or lose electrons until they have a full valence shell of eight electrons, resulting in a stable electronic configuration.
How are ionic compounds formed?
Ionic compounds are formed when one atom transfers one or more electrons to another atom, resulting in the formation of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions.
What are the limitations of Lewis structures for ionic compounds?
Lewis structures do not accurately represent the delocalized nature of electrons in ionic compounds, and they cannot account for the lattice structure of these compounds.