Hubless rotors are held onto the hub by innovative techniques that offer unique advantages in various applications. This article explores the primary mounting methods, design considerations, manufacturing processes, performance evaluation, and diverse applications of hubless rotors, providing a comprehensive overview of this cutting-edge technology.
The elimination of the traditional hub in hubless rotors allows for significant weight reduction, increased efficiency, and improved performance. These advantages make hubless rotors particularly attractive for applications in aerospace, automotive, and renewable energy sectors.
Hubless Rotor Mounting Techniques
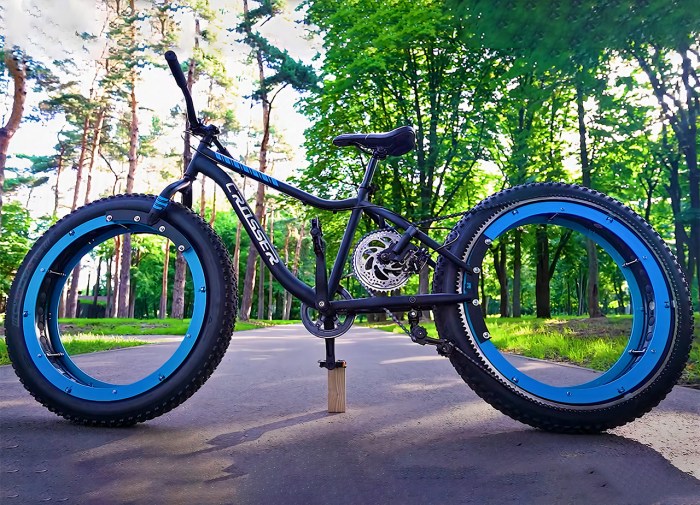

Hubless rotors are mounted onto the hub using various techniques, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. These techniques include:
- Bolting:Hubless rotors are bolted directly to the hub using high-strength bolts. This method is simple and cost-effective but can introduce stress concentrations and fatigue issues.
- Shrinking:The hubless rotor is heated to expand its diameter, then placed onto the hub. As the rotor cools, it contracts and shrinks, creating a tight fit. This method provides a secure connection but requires precise temperature control and can be time-consuming.
- Clamping:Hubless rotors are clamped onto the hub using a clamping ring or other mechanism. This method is versatile and allows for easy assembly and disassembly but may introduce additional weight and complexity.
- Interference fit:The hubless rotor is designed with a slightly larger diameter than the hub. When pressed onto the hub, the rotor expands and creates an interference fit. This method provides a secure connection but requires high-precision manufacturing and can be challenging to assemble.
The choice of mounting technique depends on factors such as rotor size, speed, and application.
Design Considerations for Hubless Rotors
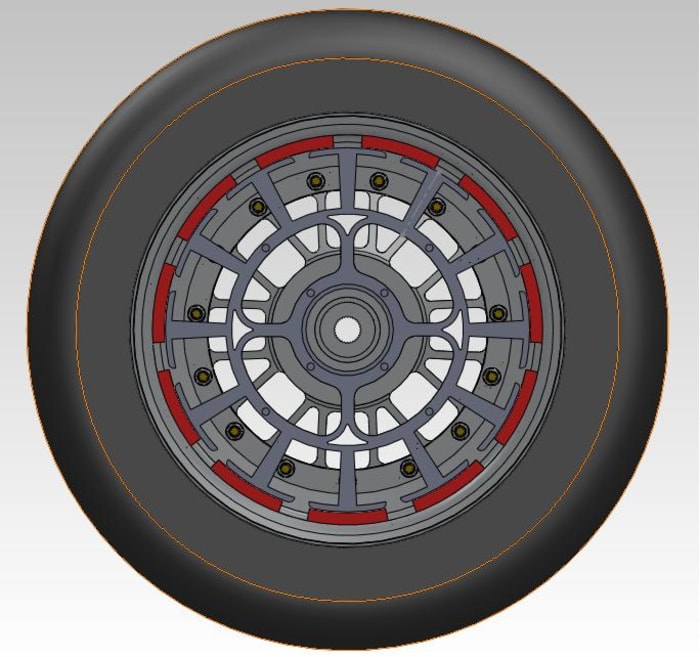
The design of hubless rotors requires careful consideration of several key factors:
Material Selection
Hubless rotors are typically made from high-strength materials such as steel, aluminum, or composite materials. The material choice impacts the rotor’s weight, strength, and durability.
Geometry Optimization
The geometry of the hubless rotor plays a crucial role in its performance. Factors such as the rotor’s thickness, shape, and cooling channels affect its efficiency and reliability.
Stress Analysis
Hubless rotors are subjected to high stresses during operation. Stress analysis is essential to ensure that the rotor can withstand these stresses and prevent failure.
Innovative Design Approaches, Hubless rotors are held onto the hub by
Researchers are continuously exploring innovative design approaches to enhance hubless rotor performance. These approaches include optimizing cooling systems, using advanced materials, and implementing novel manufacturing techniques.
Applications of Hubless Rotors: Hubless Rotors Are Held Onto The Hub By

Hubless rotors are used in a wide range of applications, including:
Aerospace
Hubless rotors are used in aircraft engines, where they provide lightweight and efficient power transmission.
Automotive
Hubless rotors are increasingly used in automotive applications, offering improved fuel economy and performance.
Renewable Energy
Hubless rotors are employed in wind turbines and other renewable energy systems, where they contribute to increased efficiency and reliability.
Emerging applications include electric vehicles, robotics, and medical devices.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the advantages of hubless rotors?
Hubless rotors offer several advantages, including weight reduction, increased efficiency, improved performance, and reduced manufacturing costs.
What are the different methods used to attach hubless rotors to the hub?
The primary methods used to attach hubless rotors to the hub include friction welding, mechanical locking, and adhesive bonding. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, depending on the specific application.
What are the key design considerations for hubless rotors?
Key design considerations for hubless rotors include material selection, geometry optimization, and stress analysis. These factors impact rotor performance, reliability, and durability.