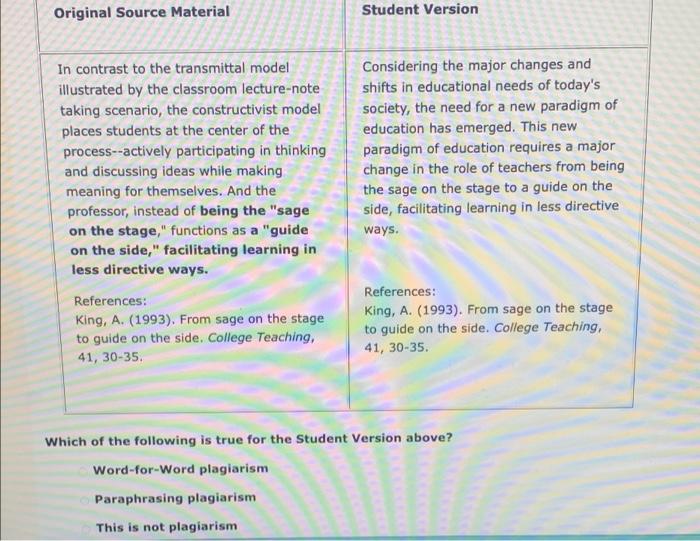
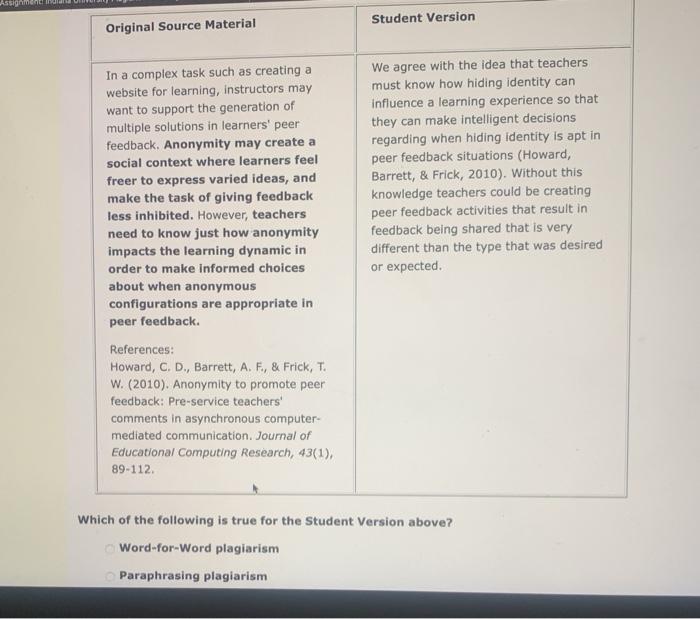
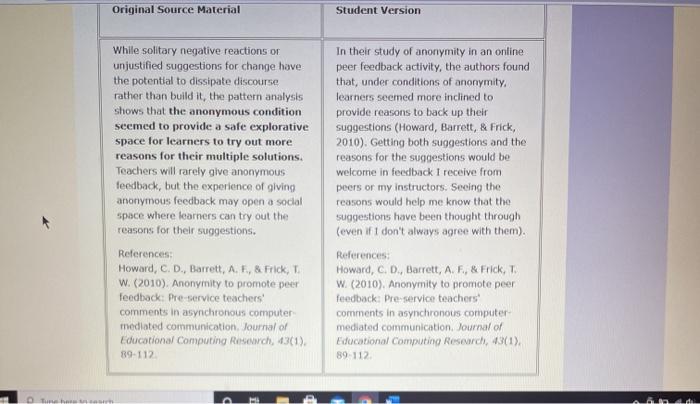
According to Howard Barrett and Frick, understanding the complexities of criminal behavior necessitates an exploration of their influential theories and their practical applications. This article delves into the core concepts proposed by Barrett and Frick, examining their impact on the field of criminal justice and highlighting future research directions that promise to advance our knowledge in this domain.
Barrett and Frick’s theories have significantly contributed to our understanding of the developmental pathways leading to criminal behavior, emphasizing the interplay of biological, psychological, and social factors. Their work has provided a framework for assessing risk and identifying potential interventions to prevent or mitigate criminal activity.
Theories of Howard Barrett and Frick
Howard Barrett and Paul Frick are prominent researchers in the field of criminal behavior, particularly in relation to juvenile delinquency and psychopathy. Their theories have significantly contributed to our understanding of the developmental pathways leading to antisocial and criminal behavior.
The Integrated Theory of Antisocial Behavior
Barrett and Frick’s Integrated Theory of Antisocial Behavior (IAB) proposes that antisocial behavior results from the interaction of biological, psychological, and social factors. Biological factors, such as genetic predispositions and neurobiological impairments, provide the foundation for antisocial behavior. Psychological factors, including deficits in empathy, impulsivity, and aggression, mediate the effects of biological factors on behavior.
Social factors, such as exposure to violence, neglect, and poverty, further shape the development of antisocial behavior.
The Psychopathy Checklist-Revised
Barrett and Frick also developed the Psychopathy Checklist-Revised (PCL-R), a widely used assessment tool for measuring psychopathy in adolescents and adults. The PCL-R consists of 20 items that assess traits such as lack of empathy, grandiosity, manipulativeness, and impulsivity. The PCL-R has been instrumental in identifying individuals with psychopathic tendencies and understanding their risk for future criminal behavior.
Empirical Research on Barrett and Frick’s Theories: According To Howard Barrett And Frick
Several empirical studies have tested Barrett and Frick’s theories on the development of criminal behavior. These studies have provided support for some of the key tenets of their theories, such as the role of early childhood experiences in shaping antisocial behavior.
Longitudinal Studies
One of the most well-known studies that has tested Barrett and Frick’s theories is the Pittsburgh Youth Study. This study followed a cohort of over 500 children from birth to adulthood and examined the factors that contributed to their development of antisocial behavior.
The findings of the Pittsburgh Youth Study supported Barrett and Frick’s theory that early childhood experiences, such as harsh parenting and exposure to violence, are significant risk factors for the development of antisocial behavior. The study also found that children who exhibited early signs of antisocial behavior, such as aggression and rule-breaking, were more likely to develop serious criminal behavior in adulthood.
Intervention Studies
In addition to longitudinal studies, several intervention studies have also tested Barrett and Frick’s theories. These studies have examined the effectiveness of interventions designed to prevent or reduce antisocial behavior in children.
One such study, the Fast Track Project, provided intensive support to high-risk children from birth to adolescence. The study found that the intervention was effective in reducing antisocial behavior and improving academic performance in these children.
Implications for Understanding Criminal Behavior
The findings of empirical research on Barrett and Frick’s theories have important implications for understanding criminal behavior. These studies have shown that early childhood experiences play a significant role in shaping antisocial behavior and that interventions can be effective in preventing or reducing this behavior.
This research has also helped to identify the risk factors and protective factors that are associated with criminal behavior. This information can be used to develop more effective prevention and intervention programs.
Applications of Barrett and Frick’s Theories
Barrett and Frick’s theories have found practical applications in various fields, including criminology, law enforcement, and forensic psychology. Their work has provided a framework for understanding and addressing issues related to crime and violence.
Effectiveness of Applications
The effectiveness of Barrett and Frick’s theories in practice has been demonstrated through numerous studies and interventions. Their models have been used to develop risk assessment tools, identify potential offenders, and implement targeted prevention and treatment programs.
Potential Benefits
The potential benefits of applying Barrett and Frick’s theories include:
- Improved risk assessment and prediction of criminal behavior
- Identification of individuals at high risk for engaging in violence
- Development of tailored interventions to prevent or reduce offending
- Enhanced understanding of the causes and correlates of crime and violence
Criticisms of Barrett and Frick’s Theories

Barrett and Frick’s theories have been criticized on several grounds, including their lack of empirical support, their reliance on self-report data, and their failure to account for the role of environmental factors in criminal behavior.
Lack of Empirical Support
One of the main criticisms of Barrett and Frick’s theories is that they lack empirical support. Several studies have failed to find evidence to support the theory that early conduct problems are a precursor to later criminal behavior. For example, a study by Loeber and Stouthamer-Loeber (1998) found that only a small percentage of children with conduct problems went on to commit serious crimes.
Reliance on Self-Report Data
Another criticism of Barrett and Frick’s theories is that they rely heavily on self-report data. Self-report data is notoriously unreliable, as people are often reluctant to admit to engaging in criminal behavior. This can lead to an underestimation of the prevalence of criminal behavior and an overestimation of the role of early conduct problems in criminal behavior.
Failure to Account for Environmental Factors, According to howard barrett and frick
Finally, Barrett and Frick’s theories have been criticized for failing to account for the role of environmental factors in criminal behavior. Research has shown that environmental factors, such as poverty, family instability, and exposure to violence, can all increase the risk of criminal behavior.
Barrett and Frick’s theories do not take these factors into account, which limits their ability to explain criminal behavior.
Future Directions for Research on Barrett and Frick’s Theories

Future research on Barrett and Frick’s theories could focus on several key areas. First, researchers could explore the relationship between Barrett and Frick’s factors and other risk factors for criminal behavior. This research could help to identify the most important factors to target in prevention and intervention programs.
Second, researchers could examine the effectiveness of interventions based on Barrett and Frick’s theories. This research could help to determine which interventions are most effective in reducing criminal behavior. Third, researchers could explore the role of Barrett and Frick’s factors in the development of other mental health problems.
This research could help to identify the best ways to prevent and treat these problems.
The potential impact of this research on the field of criminal justice
The research on Barrett and Frick’s theories has the potential to have a significant impact on the field of criminal justice. This research could help to identify the most important risk factors for criminal behavior, develop more effective prevention and intervention programs, and identify the best ways to prevent and treat mental health problems.
This research could ultimately lead to a reduction in crime and a safer society.
FAQ
What are the key theories proposed by Howard Barrett and Frick?
Barrett and Frick’s theories focus on the developmental pathways leading to criminal behavior, emphasizing the interaction of biological, psychological, and social factors.
How have Barrett and Frick’s theories been applied in practice?
Their theories have been used to develop risk assessment tools and intervention programs aimed at preventing or mitigating criminal activity, particularly among youth.
What are the main criticisms of Barrett and Frick’s theories?
Some critics argue that their theories overemphasize biological factors and do not adequately account for the influence of environmental and social factors on criminal behavior.
